

Client
Leading supply chain brokerage
Goal
Automate the manual, supply-chain scheduling process to improve staff productivity and customer satisfaction
Tools and Technologies
UI Path Orchestrator, UI Path Assistant, Microsoft Power BI, Office 365
Business Challenge
Performing crucial supply chain logistics, a provider’s operations team was struggling due to the high volume of scheduling appointments with shippers, receivers, and carriers, which involve back and forth emails, phone calls, or manual data entry into multiple Transport Management Systems (TMS).
These appointment-scheduling complexities vary based on the parties involved, from sending an email requesting appointment times to accessing a TMS and selecting what’s available as per their schedule.
Lacking proper analytics, sales representatives were unable to pinpoint peak appointment times, track cancellation rates, or discern customer preferences, often leading to shipment delays and incurred detention charges.

Solution
- Deployed multiple rule-based, automated workflows to pull information from incoming appointment requests (from emails, web forms, etc.) and automatically input it into the various TMS used to book pick-up and delivery appointments
- Developed a Power BI dashboard to visualize appointment trends, peak times, and cancellation rates, providing insights into customer behaviors, including frequent reschedules, preferred times, and typical lead times for booking appointments
- Delivered a reusable solution that could be leveraged for other business areas
Outcomes
- Bots operating 24/7 have led to over 15,000 monthly appointments being scheduled, resulting in a 50% reduction in manual scheduling hours
- The productivity of the operations team has improved by 50%, enabling staff to concentrate on high-value tasks rather than manual appointment-booking
- The increased accuracy in scheduled appointments has significantly decreased detention charges, thereby boosting overall customer satisfaction

Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Unified automation strategy enhances efficiency



Client
Leading payroll and HR solutions provider
Goal
Develop automation strategy and framework that accommodates growth and ensures efficiency
Tools and Technologies
Ansible, AWS, Dynatrace, Gremlin, Groovy, Jenkins, Keptn, KICS, Python, Terraform
Business Challenge
The SRE (Site Reliability Engineering) shared services team faced a diverse set of needs relating to automation of infrastructure and services provisioning, configuration, and deployment.
The team was encountering resource constraints, as limited in-house expertise in certain automation tools and technologies was causing delays in meeting critical automation requirements. They also needed to ensure system reliability and were challenged to scale automation solutions to accommodate increasing demands as operations grow.

Solution
- Development of a comprehensive automation strategy to align with objectives, encompassing Terraform, Ansible, Python, Groovy, and other relevant technologies in the AWS environment
- Leveraging our expertise to bridge the knowledge gap, provide training, and augment the client team in handling complex automation tasks
- Implementation of a chaos engineering framework using Gremlin, Dynatrace, Keptn, and EDA tools, to proactively identify weaknesses and enhance system resilience
- Creation of a scalable automation framework that accommodates growing needs and ensures long-term efficiency

Outcomes
- A unified automation strategy that streamlined processes, reduced manual effort, and enhanced overall efficiency by 30%
- The implementation of chaos engineering and self-healing practices, which increased reliability between 20% and 50%
- A reduction in manual interventions along with improved efficiency that will result in cost savings of 25% - 50%

Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Home » Services » Automation » Page 3

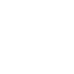
The evolution of quality engineering
Quality engineering in software development empowers organizations to achieve heightened quality, scalability and resilience.
Quality Assurance (QA) has long been essential in software engineering, ensuring the development of products and applications with established standards and metrics. But QA has been reactive, focusing on defect detection through manual and automated testing. With the evolution of software development technology and methodologies, the limitations of traditional QA are evident. This perspective paper delves into the evolution of Quality Engineering (QE), which has transformed the approach to software quality. QE goes beyond QA and Test Automation to integrate quality practices throughout the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC); it also addresses complexities in modern architectures such as microservices and cloud environments.
The journey from QA to QE is marked by several key milestones. Initially, software testing was a separate phase, conducted after development was complete. With the advent of Agile and DevOps methodologies, the need for continuous testing and early defect detection became apparent. This shift fostered the evolution of testing practices, embedding quality checks throughout the development cycle with the emerging adoption of cloud-native modern architecture, paving the way for what is now called Quality Engineering. Unlike the reactive nature of traditional QA and QA Automation, QE represents a proactive and integrated approach throughout the development lifecycle.
Organizations can significantly enhance product or application quality, optimize development workflows, and mitigate risks by addressing QE concerns at every phase of the SDLC. They could leverage structured QE approaches as mentioned above, and focus on a holistic view of quality in modern architecture.
Read our Perspective Paper for more insights on the evolution of quality engineering in software development.
Contact
Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Get in touchQuality engineering optimizes a DLT platform



Client
A leading provider of financial services digitization solutions
Goal
Reliability assurance for a digital ledger technology (DLT) platform
Tools and Technologies
Kotlin, Java, Http Client, AWS, Azure, GCP, G42, OCP, AKS, EKS, Docker, Kubernetes, Helm Chart, Terraform
Business Challenge
A leader in Blockchain-based digital financial services required assurance for non-GUI (Graphic User Interface), Command Line Interface (CLI), microservices and Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs for a Digital Ledger Technology (DLT) platform, as well as platform reliability assurance on Azure, AWS services (EKS, AKS) to ensure availability, scalability, observability, monitoring and resilience (disaster recovery). It also wanted to identify capacity recommendations and any performance bottlenecks (whether impacting throughput or individual transaction latency) and required comprehensive automation coverage for older and newer product versions and management of frequent deliveries of multiple DLT product versions on a monthly basis.

Solution
- 130+ Dapps were developed and enhanced on the existing automation framework for terminal CLI and cluster utilities
- Quality engineering was streamlined with real-time dashboarding via Grafana and Prometheus
- Coverage for older and newer versions of the DLT platform was automated for smooth, frequent deliverables for confidence in releases
- The test case management tool, Xray, was implemented for transparent automation coverage
- Utilities were developed to execute a testing suite for AKS, EKS, local MAC/ Windows/ Linux cluster environments to run on a daily or as-needed basis

Outcomes
- Automation shortened release cycles from 1x/month to 1x/week; leads testing time was reduced by 80%
- Test automation coverage with 2,000 TCs was developed, with pass rate of 96% in daily runs
- Compatibility was created across AWS-EKS, Azure-AKS, Mac, Windows, Linux and local cluster
- Increased efficiency in deliverables was displayed, along with an annual $350K savings for TCMs
- An average throughput of 25 complete workflows per second was sustained
- Achieved a 95th percentile flow-completion time that should not exceed 10 seconds

Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Home » Services » Automation » Page 3

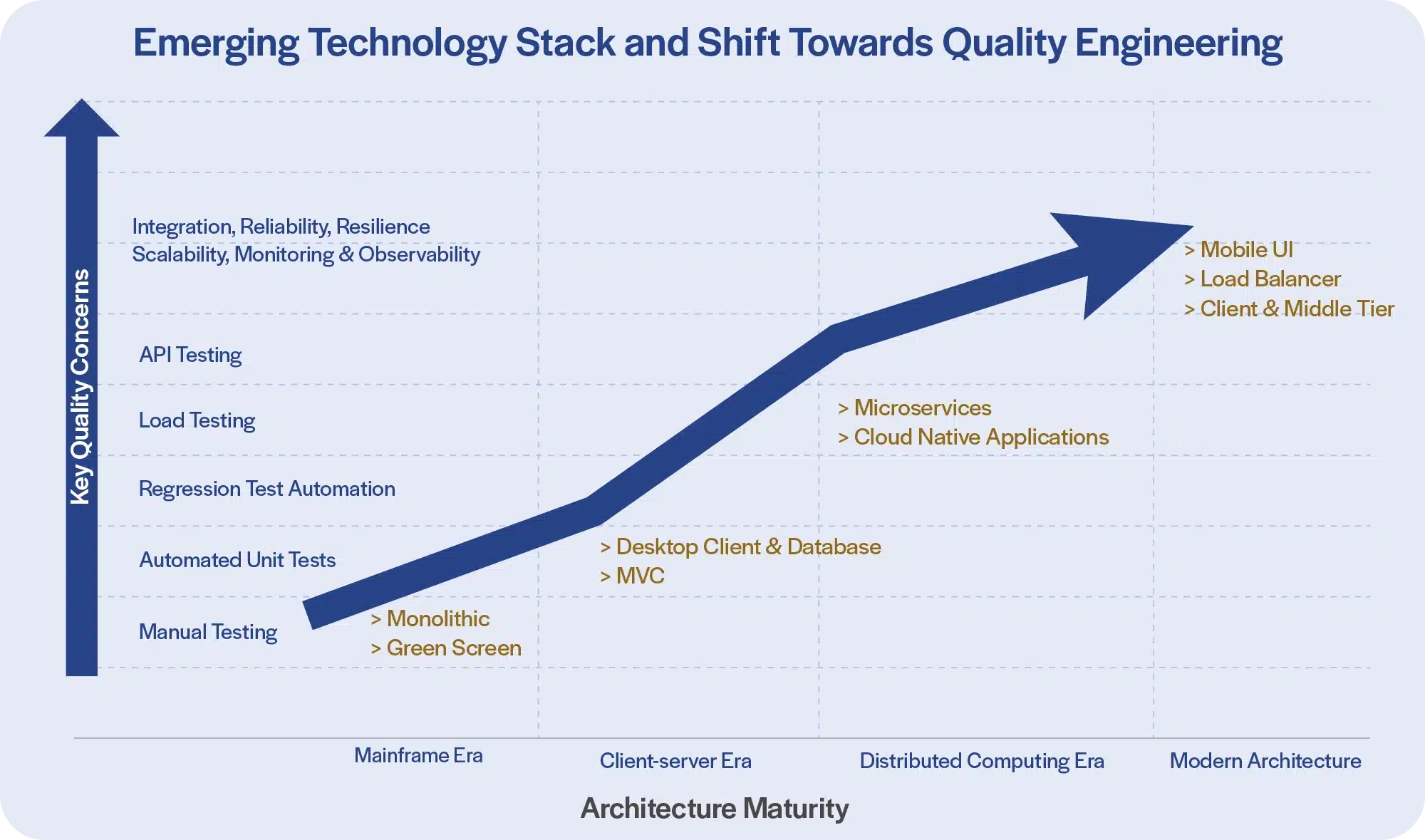
Real-world asset tokenization can transform financial markets
Integration with Distributed Ledger Technologies is critical to realizing the full potential of tokenization.
The global financial markets create and deal in multiple asset classes, including equities, bonds, forex, derivatives, and real estate investments. Each of them constitutes a multi-trillion-dollar market. These traditional markets encounter numerous challenges in terms of time and cost which impede accessibility, fund liquidity, and operational efficiencies. Consequently, the expected free flow of capital is hindered, leading to fragmented, and occasionally limited, inclusion of investors.
In response to these challenges, today's financial services industry seeks to explore innovative avenues, leveraging advancements such as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). Using DLTs, it is feasible to tokenize assets, thus enabling issuance, trading, servicing and settlement digitally, not just in whole units, but also in fractions.
Asset tokenization is the process of converting and portraying the unique properties of a real-world asset, including ownership and rights, on a Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) platform. Digital and physical real-world assets, such as real estate, stocks, bonds, and commodities, are depicted by tokens with distinctive symbols and cryptographic features. These tokens exhibit specific behavior as part of an executable program on a blockchain.
Many domains, especially financial institutions, have started recognizing the benefits of tokenization and begun to explore this technology. Some of the benefits are fractional ownership, increased liquidity, efficient transfer of ownership, ownership representation and programmability.
With the recent surge in the adoption of tokenization, a diverse array of platforms has emerged, paving the way for broader success, but at the same time creating fragmented islands of ledgers and related assets. As capabilities mature and adoption grows, interconnectivity and interoperability across ledgers representing different institutions issuing/servicing different assets could improve, creating a better integrated market landscape. This would be critical to realizing the promise of asset tokenization using DLT.
Read our Perspective Paper for more insights on asset tokenization and its potential to overcome the challenges, the underlying technology, successful use cases, and issues associated with implementation.
Contact
Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Get in touchHome » Services » Automation » Page 3

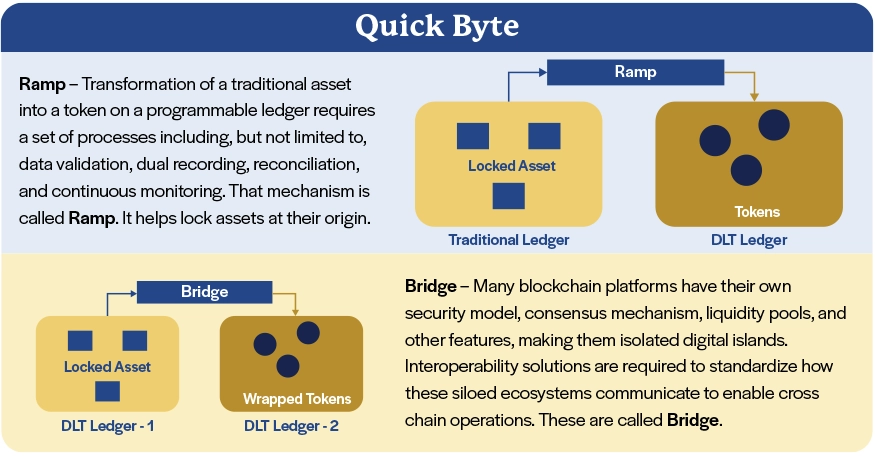
Industrializing business-critical end-user compute-based applications using low-code platforms
Low-code platforms enable rapid conversions to technology-managed applications that provide end users with rich interfaces, powerful configurations, easy integrations, and enhanced controls.
Many large and small enterprises utilize business-managed applications (BMAs) in their value chain to supplement technology-managed applications (TMAs). BMAs are applications or software that end users create or procure off-the-shelf and implement on their own; these typically are low-code or no-code software applications. Such BMAs offer the ability to automate or augment team-specific processes or information to enable enterprise-critical decision-making.
Technology teams build and manage TMAs to do a lot of heavy lifting by enabling business unit workflows and transactions and automating manual processes. TMAs are often the source systems for analytics and intelligence engines that drive off data warehouses, marts, lakes, lake-houses, etc. BMAs dominate the last mile in how these data infrastructures support critical reporting and decision making.
While BMAs deliver value and simplify complex processes, they bring with them a large set of challenges in security, opacity, controls collaboration, traceability and audit. Therefore, on an ongoing basis, business-critical BMAs that have become relatively mature in their capabilities must be industrialized with optimal time and investment. Low-code platforms provide the right blend of ease of development, flexibility and governance that enables the rapid conversion of BMAs to TMAs with predictable timelines and low-cost, high-quality output.
Read our Perspective Paper for more insights on using low-code platforms to convert BMAs to TMAs that provide end users with rich interfaces, powerful configurations, easy integrations, and enhanced controls.
Contact
Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Get in touchConversational assistant boosts AML product assurance



Client
A large global bank
Goal
Improve turnaround time to provide technical support for the application support and global product assurance teams
Tools and Technologies
React, Sentence–Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (S-BERT), Facebook AI Similarity Search (FAISS), and Llama-2-7B-chat
Business Challenge
The application support and global product assurance teams of a large global bank faced numerous challenges in delivering efficient and timely technical support as they had to manually identify solutions to recurring problems within the Known Error Database (KEDB), comprised of documents in various formats. With the high volume of support requests and limited availability of teams across multiple time zones, a large backlog of unresolved issues developed, leading to higher support costs.

Solution
Our team developed a conversational assistant using Gen AI by:
- Building an interactive customized React-based front-end
- Ringfencing a corpus of problems and solutions documented in the KEDB
- Parsing, formatting and extracting text chunks from source documents and creating vector embeddings using Sentence–Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (S-BERT)
- Storing these in a Facebook AI Similarity Search (FAISS) vector database
- Leveraging a local Large Language Model (Llama-2-7B-chat) to generate summarized responses

Outcomes
The responses generated using Llama-2-7B LLM were impressive and significantly reduced overall effort. Future enhancements to the assistant would involve:
- Creating support tickets based on information collected from users
- Categorizing tickets based on the nature of the problem
- Automating repetitive tasks such as access requests / data volume enquiries / dashboard updates
- Auto-triaging support requests by asking users a series of questions to determine the severity and urgency of the problem

Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Gen AI powered summarization boosts compliance workflow



Client
A leading specialty property and casualty insurer
Goal
Improve underwriters’ ability to review policy submissions by providing easier access to information stored across multiple, voluminous documents.
Tools and Technologies
Azure OpenAI Service, React, Azure Cognitive Services, Llama-2-7B-chat, OpenAI GPT 3.5-Turbo, text-embedding-ada-002 and all-MiniLM-L6-v2
Business Challenge
The underwriters working with a leading specialty property and casualty insurer have to refer to multiple documents and handbooks, each running into several hundreds of pages, to understand the relevant policies and procedures, key to the underwriting process. Significant effort was required to continually refer to these documents for each policy submission.

Solution
A Gen AI enabled conversational assistant for summarizing information was developed by:
- Building a React-based customized interactive front end
- Ringfencing a knowledge corpus of specific documents (e.g., an insurance handbook, loss adjustment and business indicator manuals, etc.)
- Leveraging OpenAI embeddings and LLMs through Azure OpenAI Service along with Azure Cognitive Services for search and summarization with citations
- Developing a similar interface in the Iris-Azure environment with a local LLM (Llama-2-7B-chat) and embedding model (all-MiniLM-L6-v2) to compare responses

Outcomes
Underwriters significantly streamlined the activities needed to ensure that policy constructs align with applicable policies and procedures and for potential compliance issues in complex cases.
The linguistic search and summarization capabilities of the OpenAI GPT 3.5-Turbo LLM (170 bn parameters) were found to be impressive. Notably, the local LLM (Llama-2-7B-chat), with much fewer parameters (7 bn), also produced acceptable results for this use case.

Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Automated financial analysis reduces manual effort



Client
Commerical lending and credit risk units of large North American bank
Goal
Automated retrieval of information from multiple financial statements enabling data-driven insights and decision-making
Tools and Technologies
OpenAI API (GPT-3.5 Turbo), LlamaIndex, LangChain, PDF Reader
Business Challenge
A leading North American bank had large commercial lending and credit risk units. Analysts in those units typically refer to numerous sections in a financial statement, including balance sheets, cash flows, and income statements, supplemented by footnotes and leadership commentaries, to extract decision-making insights. Switching between multiple pages of different documents took a lot of work, making the analysis extra difficult.

Solution
Many tasks were automated using Gen AI tools. Our steps:
- Ingest multiple URLs of financial statements
- Convert these to text using the PDF Reader library
- Build vector indices using LlamaIndex
- Create text segments and corresponding vector embeddings using OpenAI’s API for storage in a multimodal vector database e.g., Deep Lake
- Compose graphs of keyword indices for vector stores to combine data across documents
- Break down complex queries into multiple searchable parts using LlamaIndex’s DecomposeQueryTransform library

Outcomes
The solution delivered impressive results in financial analysis, notably reducing manual efforts when multiple documents were involved. Since the approach is still largely linguistic in nature, considerable Prompt engineering may be required to generate accurate responses.
Response limitations due to the lack of semantic awareness in Large Language Models (LLMs) may stir considerations about the usage of qualifying information in queries.

Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Next generation chatbot eases data access



Client
Large U.S.-based Brokerage and Wealth Management Firm
Goal
Enable a large number of users to readily access summarized information contained in voluminous documents
Tools and Technologies
Google Dialogflow ES, Pinecone, Llamaindex, OpenAI API (GPT-3.5 Turbo)
Business Challenge
A large U.S.-based brokerage and wealth management firm has a large number of users for its retail trading platform that offers sophisticated trading capabilities. Although extensive information was documented in hundreds of pages of product and process manuals, it was difficult for users to access and understand information related to their specific needs (e.g., How is margin calculated? or What are Rolling Strategies? or Explain Beta Weighting).

Solution
Our Gen AI solution encompassed:
- Building a user-friendly interactive chatbot using Dialogflow in Google Cloud
- Ringfencing a knowledge corpus comprising specific documents to be searched against and summarized (e.g., 200-page product manual, website FAQ content)
- Using a vector database to store vectors from the corpus and extract relevant context for user queries
- Interfacing the vector database with OpenAI API to analyze vector-matched contexts and generate summarized responses

Outcomes
The OpenAI GPT-3.5 turbo LLM (170 bn parameters) delivered impressive linguistic search and summarization capabilities in dealing with information requests. Prompt engineering and training are crucial to secure those outcomes.
In the case of a rich domain such as a trading platform, users may expect additional capabilities, such as:
- API integration to support requests requiring retrieval of account/user specific information, and
- Augmentation of linguistic approaches with semantics to deliver enhanced capabilities.

Our experts can help you find the right solutions to meet your needs.
Industries
Company

Bring the future into focus.
